Scientific
name
Cordia sinensis1 (Lam.)
Cordia
gharaf Ehreneb. ex Aschers. (Synonym)
Similar
species are: Cordia somalinesis Bak., Cordia crenata Del.
Family name
Boraginaceae
Local name(s)
Maderta
(Konsogna), Mareer, Marer (Somali), Harores, Mader-boor, Madeer-qoowe, Madee'r (Borena)
General description
A
low leafy shrub or bush, rarely a small tree up to 6m high, often multi-stemmed.
The bark is finely fissured longitudinally, or smooth, dark grey on branches.
Leaves are variable, smooth or slightly rough, narrow and long, ovate to obovate
or broadly so. Flowers are of cream colour, browning when over. Fruits are
conical, bright red or orange when ripe, produced in masses. Seed hard, rough,
yellowish cream.
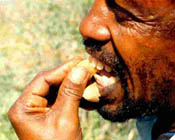
Edible part(s),
preparation methods and palatability
Fruits
and gum are edible. The sweet and sticky tasty pulp of the fruit is eaten fresh.
The fruit cover and the seeds are discarded. In Kenya (Turkana) large quantities
of fruits are gathered, pounded to a sticky mass, sun-dried and stored in a
wooden container. Whenever needed, water is added to soften it, then served. The
fruit pulp is sometimes used to brew local beer. The fresh fruits are squeezed
in water to dissolve the pulp. This is mixed with tamarind (Tamarindus indica)
juice and fermented. The fresh juice may also be drunk. The clear gum from the
tree is also edible. Children consume fruits whenever they are ripe. When food
shortage occurs adults also eat the fruit.
Agroecology
C.
sinensis
grows in the Middle East, Pakistan, India, Sri Lanka and in Africa from West
Africa to Ethiopia, Somalia and Egypt, south to Namibia and north-east South
Africa. The species is found in dry riverine vegetation, usually with Salvadora
persica, or in open bushland, usually from sea level to 1,400m in alluvial,
sandy, red loam and rocky soils.
Propagation
method(s)
Propagates
by
seeds that are best sown directly on site.
Sample location(s)
(1)
Jarso Kebele, Konso; (2) Shagana village, Konso
Remarks
The
species is a very important plant in dry areas as a source of food, fodder and
wood for building. Most of the Cordia species have edible fruits. A
source of fodder for goats, sheep, cattle and camels. Stems can be used for
walking sticks, wooden spoons and stirrers.
1 Parts
of the following description have been taken from Maundu et al., 1999: p. 104
Back
to top
|